The joint probability mass function
p(x, y)
for a pair of discrete random quantities
X, Y
is defined by the following table.
| p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| –1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| x | –1 | .10 | .20 | .20 |
| 0 | .06 | .08 | .16 | |
| 1 | .04 | .12 | .04 | |
- Find the correlation coefficient
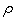 for X and Y , correct
to three decimal places.
for X and Y , correct
to three decimal places.
- Are X and Y stochastically independent?