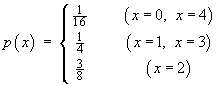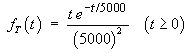ENGI 3423 Probability and Statistics
Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science
2008 Fall
Term Test 2
2008 October 29
[Single and Joint Probability Distributions, Central Limit Theorem]
A function p(x) of a discrete
variable x is defined by
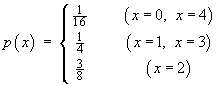
- Verify that p(x) is a
well-defined probability mass function.
[3]
- Write down [or sketch the graph of] the
corresponding cumulative distribution function
F (x).
[3]
- For a random quantity X with this
probability distribution, find the probability that the
value of X is at most 1.
[2]
- Find the population mean of X ,
µ = E[X].
[2]
- Find the population variance of X ,
s 2 = V[X].
[5]
The joint probability mass function of two discrete random
quantities X, Y is given by the table
| p(x, y) |
Y | |
| -1 | 0 | 1 |
| X | -1 |
.06 | .09 | .15 |
|
| 0 | .04 | .00 |
.16 | |
| 1 | .10 | .21 |
.19 | |
| | |
| | |
- Extend the table to display the marginal probability mass
functions pX(x) and
pY(y).
[2]
- Verify that p(x, y)
is a valid probability mass function.
[2]
- Find the covariance of X and Y.
[5]
- Are X, Y independent? Why or why not?
[3]
A storage shed contains ten pipes of the same size, eight
made of cast iron and two of stainless steel. A
random sample of three pipes is drawn without replacement
from that population. Let X be
the number of stainless steel pipes in the random sample.
- Explain why the probability distribution of X
is not binomial.
[3]
- Find P[X = 3].
[2]
- Find the probability mass function for X.
[4]
- Find the expected value µ = E[X].
[3]
Fluorescent lamps from a production line have lifetimes
T that are independent random quantities,
following an exponential distribution with a mean lifetime
of 5,000 hours.
- Find the probability that a randomly chosen lamp has a
lifetime exceeding 12,000 hours.
[3]
- Find the median lifetime
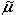 for these lamps.
for these lamps.
[3]
- A random sample of 100 lamps is taken. Find, correct
to two significant figures, the probability that the
sample mean lifetime exceeds 6,000 hours.
[5]
BONUS QUESTION:
- Show that the exact probability density function of the sum
of the lifetimes of two lamps drawn randomly from
this population is
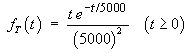
[+5]
 [Index of assignments]
[Solution of this Test]
[Index of assignments]
[Solution of this Test]
 [Return to your previous page]
[Return to your previous page]
Created 2008 10 17 and most recently modified 2008 10 17 by
Dr. G.H. George