Note: You need the
Symbol font (68 kB)
in order to display various symbols correctly, such as
![]() (otherwise they appear as
p, r, q and f ).
(otherwise they appear as
p, r, q and f ).
Note: You need the
Symbol font (68 kB)
in order to display various symbols correctly, such as
![]() (otherwise they appear as
p, r, q and f ).
(otherwise they appear as
p, r, q and f ).
The function f (x) is defined on the interval [0, 1] by
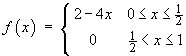
Sketch the even periodic extension of this function.
[3]
Find the Fourier cosine series for f (x) .
[7]
The Cartesian equation of a surface S
is
![]() .
.
Classify this quadric surface [an answer of less than five words is sufficient].
[1]
Find the equation of the tangent plane to
S at the point
[6]
Hence write down the equations of the normal line to
S at the point
[3]
A vector field at all points (x, y, z)
in ![]() is
is
![]()
Express this vector field in the cylindrical polar coordinate system.
[5]
Using the Cartesian coordinate system, find curl F .
[3]
Using the cylindrical polar coordinate system, confirm your value for curl F .
[4]
A vector field is defined on the xy plane by
![]()
A simple closed path C is defined by
a triangle whose vertices are at the points
(0, 0), (1, 0) and (0, 1).
Can Green’s theorem be used to evaluate the work done by F in one circuit of C ? Why or why not?
[4]
Find the exact value of the work done by F in one circuit of C .
[8]
A parabolic cylindrical coordinate system
(u, v, w) is related to the
Cartesian coordinate system
![]()
[4]
[4]
[4]
[2]
A thin shell S is in the shape of
part of a cylinder, radius 2 m, centred on the
z axis, from ![]() of the shell at any point
of the shell at any point
![]() kg m–2.
kg m–2.
What is the range of possible values of the constant a , if the mass of every part of the shell is non-negative?
[4]
Find the mass m of the shell.
[5]
Find the location
![]() of the centre of mass of the shell.
of the centre of mass of the shell.
[7]
Water is flowing along a horizontal cylindrical pipe that has a circular cross section of constant radius a (metre). The line of symmetry of the cylindrical pipe is aligned along the y-axis. The velocity of the water at all points in the pipe is
![]()
where vo is the
maximum speed (in ms–1) of the water in
the pipe.
Find the rate Q
(in m3s–1) at which water is
flowing across any circular cross section of the pipe.
[14]
For the partial differential equation
![]()
[2]
[5]
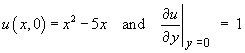
[5+5]
[Total: 100 marks]
|
|
[On to the Solutions]
|
Created 2009 05 07 and most recently modified 2009 05 07 by Dr. G.H. George