From prior experience, it is believed that the mean
potential of a certain type of battery is 12.0 V.
The strength of this belief is represented by the standard
deviation ![]() .
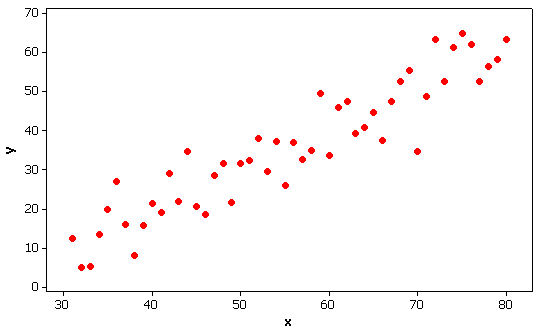
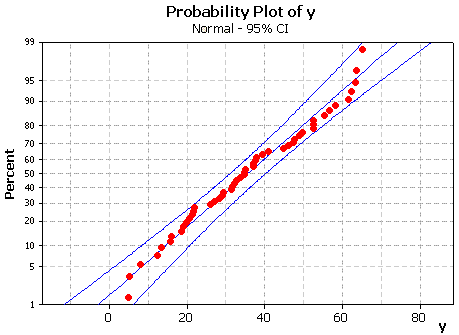
A random sample of 81 such batteries has a sample mean
potential of 12.2 V with a sample standard deviation of
0.3 V.
.
A random sample of 81 such batteries has a sample mean
potential of 12.2 V with a sample standard deviation of
0.3 V.
- Construct a Bayesian 95% confidence interval estimate for
the true mean potential µ.
[8]
- Construct a classical 95% confidence interval estimate for
the true mean µ.
[5]
- Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that the true
mean potential µ is not
12.0 V?
[2]
![[blocks A, B in parallel; then C in series;
all in parallel with D]](f07/q4blocks.gif)
![P[X|A] = 2/3 P[Y|A] = P[Z|A] = 1/6
P[X|B] = P[Y|B] = 1/5 P[Z|B] = 3/5](f07/q7probs.gif)